
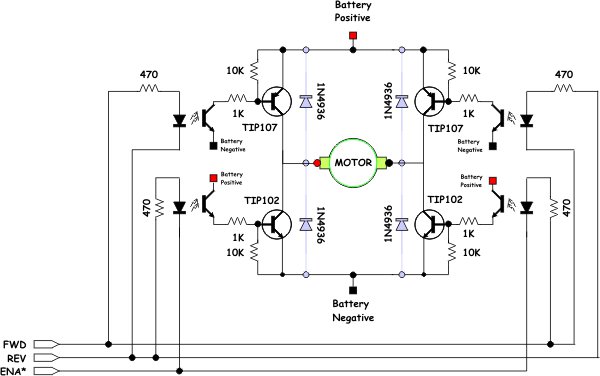
If you can drive both your PNP and NPN transistors from the same logic line (i.e. Some microcontrollers include a full bridge driver (Microchip call this Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM or ECCP on their 8bit PIC chips) which drives 4 outputs and you can hook up to the H-bridge. You could theoretically use just the two PWM outputs, however you need to be careful about the polarity of the signal compared to the transistor you're driving. To control a plain H-bridge you need 4 signals to control the 4 transistors, to control it with PWM you need two PWM signals and two plain digital signals. Most modern microcontrollers have the ability to generate PWM built in, including the Arduino and derivatives. This makes it easy to generate and efficient as transistors are most efficient when on or off rather than partially conducting. Essentially if you take the average of the signal over time then it has a varying analog level, however in the short term it is digital. PWM is a method of digitally controlling an output with a variable equivalent voltage. You can build an H-bridge like this out of relays instead of switches and control them with a lower current to drive big motors but most often the switches are replaced with transistors, a pair of PNP transistors (or p-type MOSFETS) at the top and a pair of NPN (or n-type MOSFETS) at the bottom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
